See Explanation
/uploads/2805_body_85546194037dd4928bc93b3d52c8ab9f.jpg
Pediatrics
infectious disease
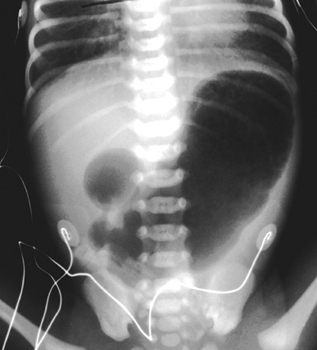
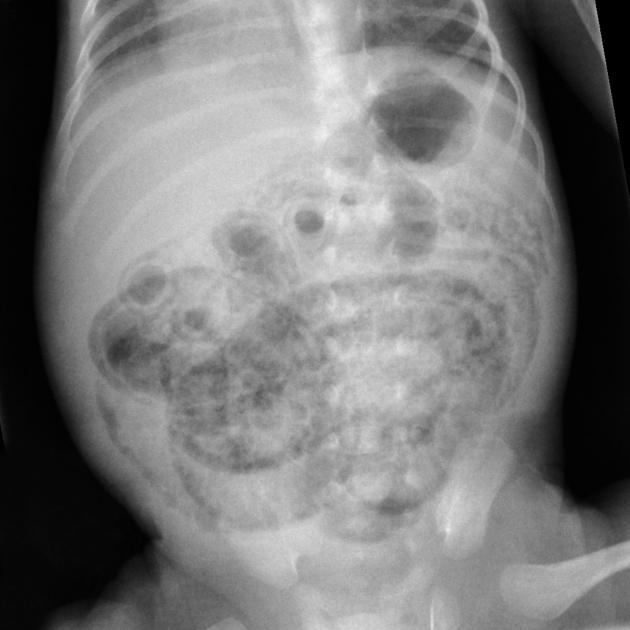
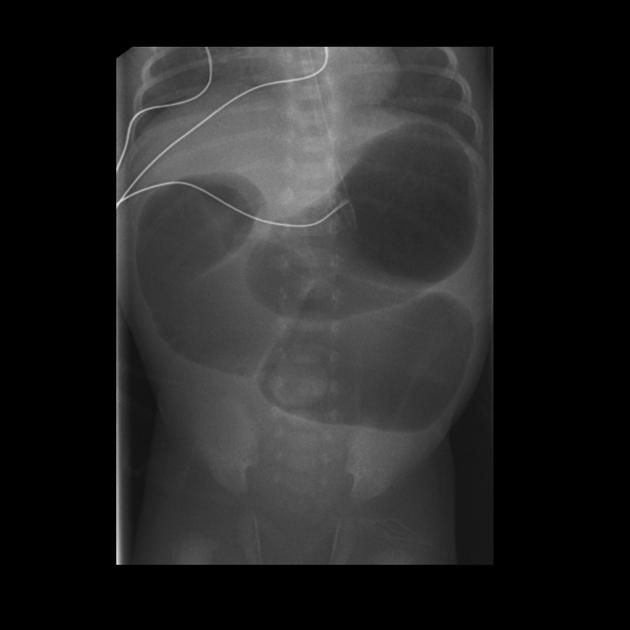
necrotizing enterocolitis
A 10-day-old female infant, born prematurely at 32 weeks gestation, presents to an outpatient clinic with a 24-hour history of increased lethargy, marked feeding intolerance, and frequent bilious emesis. Her caregivers also report intermittent episodes of apnea and temperature instability, along with new onset hematochezia. On physical examination, the infant appears ill, with a distended and diffusely tender abdomen. Peritoneal signs are not overtly present. Complete blood count reveals a white blood cell count of 1.5 x 10^9/L, hemoglobin of 125 g/L, and platelet count of 80 x 10^9/L. C-reactive protein is significantly elevated at 80 mg/L. Arterial blood gas shows a pH of 7.20, pCO2 40 mmHg, HCO3 15 mmol/L, and base excess -10 mmol/L. Vital signs are T 35.8°C, HR 180 bpm, RR 60 breaths/min, and SpO2 90% on room air. What is the most likely diagnosis and the immediate therapeutic intervention?
| Lab Parameter | Value | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|
| White Blood Cell Count | 1.5 x 10^9/L | 4.5-11.0 x 10^9/L |
| Hemoglobin | 125 g/L | 140-200 g/L (neonate) |
| Platelet Count | 80 x 10^9/L | 150-450 x 10^9/L |
| C-reactive Protein (CRP) | 80 mg/L | <5 mg/L |
| pH (arterial) | 7.20 | 7.35-7.45 |
| pCO2 (arterial) | 40 mmHg | 35-45 mmHg |
| HCO3 (arterial) | 15 mmol/L | 22-26 mmol/L |
| Base Excess (arterial) | -10 mmol/L | -2 to +2 mmol/L |
Edit question